2.1 What is valve❓❓❓
Valves are for starting and stopping flow, regulating or throttling flow, preventing back flow or relieving and regulating pressure in fluid or gaseous handling applications.
2.2 Function of valves
- Stopping and starting flow
- Reduce or increase a flow
- Controlling the direction of flow
- Regulating a flow or process pressure
- Relieve a pipe system of a certain pressure
2.3 Type of valve & applications
- Ball
- Butterfly
- Check, Diaphragm
- Gate
- Globe
- Knife Gate
- Parallel Slide
- Pinch
- Piston
- Plug
- Sluice
2.3.1 BALL VALVES
A ball valve is a valve consisting of metal ball with a hole in it. When the valve is open, a fluid can flow through the hole.
Advantages - quick acting, straight through flow in either direction, low pressure drop, bubble tight shut off and operating torque, easily actuated.
Disadvantage - temperature limitiation on seating material, long relative face to face dimension.
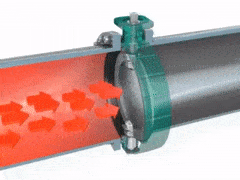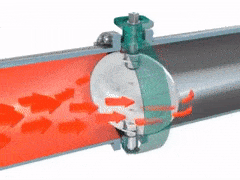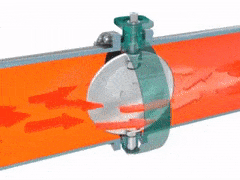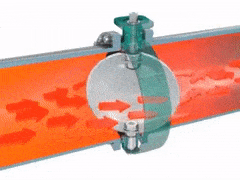
2.3.2 BUTTERFLY VALVES
A disk-shaped valve turning on axis along its diameter, serving especially as a damper in a pipe or as a choke or throttle in a carburetor.
Advantages - quick acting, good regulating characteristics, compact & light, low pressure isolation. Butterfly valves are simple, reliable and range in size.
2.3.3 CHECK VALVES
Swing Check Valves & tilting disc check: - A check valve in which the disc, the movable part to block the flow, swings on a hinge or trunnion , either onto the seat to block reverse flow or off the seat to allow forward flow.
swing check valve
tilting disc check valve
Piston Check Valves: - Piston & Spring checks cease reverse flow with a spring loaded plunger.
Ball Check Valves:- Ball Check valves are generally used to protect pumps or similar equipment, allowing the flow in only one direction and preventing flow reversal due to back pressure.
2.3.4 GLOVE VALVES
A globe valve, different from ball valve, is a type of valve used for regulating flow in a pipeline, consisting of movable disk-type element and stationary ring seat in a generally spherical body.
Disadvantages - high pressure drop (head loss), unidirectional.
2.3.5 GATE VALVES
A gate valve is valve with a sliding plate that controls the flow of fluid in a pipe or channel.
Wedge Gate Valves: - Commonly used in industrial piping for stop or isolating – to turn on and shut off the flow as opposed to regulating flow.
Advantages - low pressure drop, straight through flow either direction.
Disadvantages- slow acting, bulky. Do not partially open as this will cause damage to seat/disc.
Knife Gate Valves: - A knife gate valve is a component that utilizes a blade to cut through clogging of heavy liquids.
2.3.6 PLUG VALVES
Plug valves are valves with cylindrical or conically-tapered “plugs” which can be rotated inside the valve body to control flow through the valve. The plugs in plug valves have one or more hollow passageways going sideways through the plug, so that fluid can flow through the plug when the valve is open. Plug valves are simple and often economical.
Plug valves are valves with cylindrical or conically-tapered “plugs” which can be rotated inside the valve body to control flow through the valve. The plugs in plug valves have one or more hollow passageways going sideways through the plug, so that fluid can flow through the plug when the valve is open. Plug valves are simple and often economical.
2.4 Classification of valves based on motion
Next subtopic compressor: mechanicalcomponentandmaintenance.blogspot.com